 |
Excerpts
from The National Health Survey Report,
page II-48-49
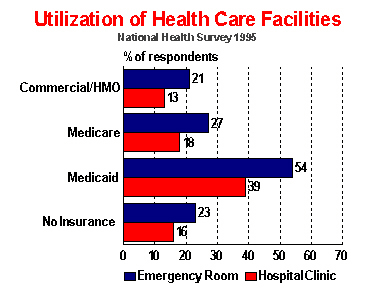
U.S.
residents with Medicaid coverage were
more likely than those with Commercial/HMOs,
Medicare, or no insurance to go to a hospital
emergency room (54% vs. 21%, 27%, and
23%). (Charts 113 and 115) U.S. residents
enrolled in Medicaid were more likely
than those with Commercial/HMOs, Medicare,
or no insurance to go to a hospital clinic
(39% vs. 13%, 18%, and 16%). U.S. residents
with poverty-level income were more likely
than those with low or above low income
to report going to a hospital clinic for
medical attention (26% vs. 12% and 14%).
There was an indirect relationship between
respondents' health status and going to
a hospital emergency room. As respondents'
health status increased, the proportion
of U.S. residents who go to a hospital
emergency room decreased (fair/poor=39%,
very good/good=23%, excellent=13%). (Charts
113, 114, and 115)
See
More Data?
National
Health Survey Intoduction Page
|